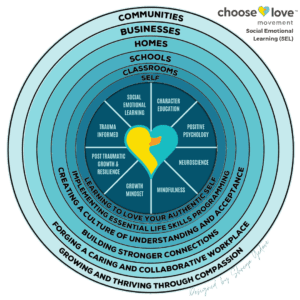
What is Social Emotional Learning (SEL)? Social and Emotional Learning means learning how to have healthy relationships, how to make deep and meaningful connections, skills and tools for resilience and learning how to manage our emotions.
We are NOT born with these skills, and they are essential to a happy and healthy life.
SEL teaches personal responsibility, giving children an awareness of who they are and an understanding of and compassion for others. Social and emotional learning proactively reduces and prevents suffering, before it even starts.
The Collaborative for Academic Social and Emotional Learning (CASEL) defines social and emotional learning (SEL) as “the process through which children and adults acquire and effectively apply the knowledge, attitudes, and skills necessary to understand and manage emotions, set and achieve positive goals, feel and show empathy for others, establish and maintain positive relationships, and make responsible decisions (casel.org).”
Over 30 years of research substantiates the benefits of social and emotional learning (SEL), (CASEL: What is SEL, 2016).
SEL is based in the idea that rich and meaningful learning occurs when people are engaged in positive and supporting relationships. It llays the groundwork for academic learning and responsible citizenship.
Social and emotional learning has been proven to increase grades, attendance, and focus, while reducing aggression, anxiety, substance abuse, and other issues (CASEL: What is SEL, 2016).
SEL plays a critical role in improving children’s academic performance and lifelong learning (Zins, Bloodworth, Weissberg & Walberg, 2004).
Children who are aware of their emotions and have good planning skills by the time they enter school are also at lower risk for problems with aggression and anxiety disorders (Greenberg, Kusch, & Mihalic, 1998).
Students aren’t the only ones who benefit from SEL. Schools are challenged by teacher attrition and unsafe learning environments (CASEL: What is SEL, 2016). When educators teach SEL, they help students create safe, loving, and healthy problem-solving communities that enhance teachers’ ability to teach as well as students’ ability to learn (CASEL: Outcomes Associated with Five Competencies, 2016).
According to CASEL, the 5 core competencies to be taught in an SEL curriculum are defined as follows:
- Self-Awareness is the ability to accurately recognize one’s own emotions and thoughts and how these influence behavior.
- Self-Management is the ability to successfully regulate one’s emotions, thoughts, and behaviors in different situations.
- Social Awareness if the ability to take the perspective of and empathize with others, including those from diverse backgrounds and cultures.
- Relationship Skills require the ability to establish and maintain healthy and rewarding relationships with diverse individuals and groups.
- Responsible Decision-Making requires the ability to make constructive choices about personal behavior and social interactions based on ethical standards, safety concerns, and social norms.
Choose Love has added to these 5 core competencies in our Choose Love For Schools™ curriculum, creating what we call a Next Generation model for SEL that also includes:
- Character Education
- Positive Psychology
- Neuroscience
- Mindfulness
- Growth Mindset
- Post-Traumatic Growth
The Choose Love Movement SEL Ripple Model demonstrates how next generation SEL does not take place in a vacuum, but rather extends outward from the classroom, to school-wide practices and policies, and even further to family, community and business partnerships.